Introduction
Nightlock berries, also known as belladonna berries, are notorious for their toxic properties. People use these berries both in medicine and in poison. During some claim that nightlock berries have miraculous healing properties, others warn against their deadly effects. So, what exactly are night lock berries, and are they poison or panacea?
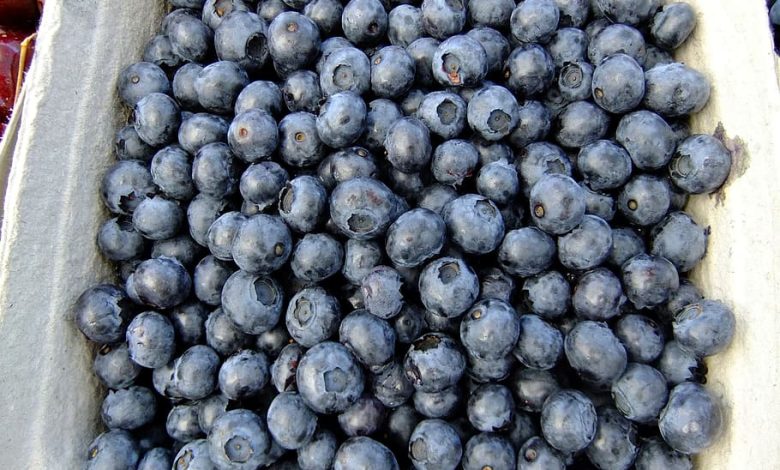
The plant has purple bell-shaped flowers that bloom from May to September, and the fruit ripens from August to October. The fruit is a shiny black or dark purple berry about the size of a cherry. Each berry contains several seeds and can be very sweet to the taste.
Nightlock berries are among the most controversial plants in the botanical world. They have been used for centuries as a poison and medicine herb. But what are the risks and benefits associated with nightlong berries? This article looks closely at everything anyone needs to know about night lock berries, including their properties, uses, and potential dangers.
What are Nightlock Berries?
Nightlock berries, also known as belladonna berries, are the fruit of the Atropa belladonna plant. The plant is native to Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia, but it can also be found in many other parts of the world. The berries are small and shiny, and they start green before turning dark purple when they ripen.
Nightlock berries contain several toxic alkaloids, including atropine, scopolamine, and hyoscyamine. These substances can cause various symptoms when ingested, including hallucinations, delirium, dry mouth, blurred vision, and even coma or death in extreme cases.
The Dark Side of Nightlock Berries: Poison or Panacea?
With their medicinal benefits, Nightlock berries can still be dangerous if ingested in large amounts. Even a small amount of the berries can cause serious symptoms, and ingesting several can be fatal.
The toxic alkaloids in nightlock berries can cause various symptoms, including dilated pupils, dry mouth, flushed skin, rapid heartbeat, and confusion. In more severe cases, they can cause hallucinations, delirium, and coma.
Children are particularly susceptible to the toxic effects of nightlock berries, as they are more likely to mistake them for edible berries. The berries should be kept out of the reach of small children, and parents should also educate their children.
Myth vs. Reality: The Truth About the Effects of Nightlock Berries
Nightlock berries, also known as “devil’s berries,” have been a subject of folklore and superstition for centuries. These small, shiny, purple-black berries grow in clusters and are known to be deadly poisonous.
In ancient Rome, night lock berries were poisonous to kill criminals and enemies. According to legend, Emperor Nero used nightlock berries to kill his enemies and even his mother. In medieval Europe, they were believed to be the favorite food of witches. They were associated with black magic and evil spells.
Despite their deadly reputation, nightlock berries have also been used for medicinal purposes. In traditional Chinese medicine, they are believed to have powerful healing properties. They treat various ailments, including inflammation, fever, and arthritis. Nighlock berries are used as a painkiller to stop vomiting in case of poisoning.
In modern times, nightlock berries have found their way into popular culture, particularly through literature and film. In the Hunger Games series, nightlock berries play a significant role in the plot, as they are used by the protagonists as a last resort to avoid being captured by the antagonists.
How to Identify Nightlock Berries and Avoid Dangerous Mistakes
It’s important to identify nightlock berries to avoid accidental ingestion. Nightlock berries are shiny black or dark purple and are about the size of a cherry. They grow in clusters on the Atropa belladonna plant and are usually hidden among the foliage.
The Science Behind Nightlock Berries: Toxicity and Medicinal Properties
Nightlock berries are highly toxic, and their consumption can lead to severe health problems, including death. These alkaloids have anticholinergic effects, which can cause dry mouth, blurred vision, tachycardia, and hallucinations.
The toxicity of night lock berries can vary depending on the amount consumed and the individual’s age, weight, and health status. Ingesting just two to five berries can be fatal to a child while consuming 10 to 20 berries can be lethal to an adult. The symptoms of nightlock berry poisoning can include dilated pupils, dry mouth, fever, confusion, delirium, seizures, and even coma.
Despite their toxicity, nightlock berries have been used for centuries for their medicinal properties. In traditional medicine, nightlock berries have been used to treat various ailments, including asthma, menstrual cramps, digestive disorders, and inflammation.
Due to the alkaloids present in this plant, nightlock berries possess medicinal properties. Atropine, one of the alkaloids found in nightlock berries, has been used in modern medicine to treat bradycardia, a condition characterized by a slow heart rate. Scopolamine, another alkaloid found in night lock berries, has been used as a pre-anesthetic medication to treat motion sickness.
Nightlock Berries in Folklore and Superstition: Tales of Danger and Healing
Nightlock berries, also known as “devil’s berries,” have been a subject of folklore and superstition for centuries. These small, shiny, purple-black berries grow in clusters and are known to be deadly poisonous. In many cultures, they are associated with danger, darkness, and death. Still, they also have a reputation for healing and protection.
In ancient Rome, nightlock berries were poisonous to kill criminals and enemies. According to legend, Emperor Nero used nightlock berries to kill his enemies and even his mother. They were associated with black magic and evil spells. It was said witches would use nightlock berries to brew potions and cast curses.
In traditional Chinese medicine, they are believed to have powerful healing properties. They treat various ailments, including inflammation, fever, and arthritis. Nightlock berries are used as a painkiller to stop vomiting in case of poisoning.
How to Use Nightlock Berries Safely: Precautions and Recipes
Despite their poisonous properties, nightlock berries have been used for various purposes throughout history. In ancient times, they were used by witches and sorcerers for their hallucinogenic effects, as well as for their supposed ability to grant supernatural powers.
In medieval Europe, nightlock berries were sometimes used as a cosmetic to dilate the pupils and make the eyes appear more attractive. It is where the plant’s scientific name, Atropa belladonna, comes from – “belladonna” means “beautiful lady” in Italian.
Nightlock berries have also been used in traditional medicine for their pain-relieving, anti-inflammatory, and antispasmodic properties. They have been used to treat various conditions, including menstrual cramps, asthma, Parkinson’s disease, and gastrointestinal disorders.
Nightlock Berries vs. Other Poisonous Plants: How to Tell Them Apart
Nightlock berries are often mistaken for other poisonous plants due to their similar appearance. However, several key differences between nightlock berries and other poisonous plants can help you tell them apart.
The deadly nightshade is one of the most common poisonous plants that can be mistaken for nightlock berries. Both plants have small, shiny, purple-black berries that grow in clusters, but the berries of the deadly nightshade are larger and have a more rounded shape. In addition, the leaves of the deadly nightshade are wider and have a distinct point at the tip, while the leaves of the nightlock plant are narrower and more oval-shaped.
Another plant that can be mistaken for nightlock berries is the bittersweet nightshade. While the berries of the bittersweet nightshade are similar in size and color to nightlock berries, they are more elongated and have a distinctive nipple-like protrusion at the end.
Toxicity is another important factor to consider when trying to identify poisonous plants. Nightlock berries are highly poisonous and can be fatal if ingested.
How Nightlock Berries Affect the Body: Understanding the Science of Toxicity
Nightlock berries are one of the most poisonous plants in the world, containing a cocktail of deadly chemicals that can cause serious harm to the human body. The toxins in nightlock berries, known as alkaloids, affect the nervous system, leading to confusion, hallucinations, seizures, and even death.
The main alkaloid in night lock berries is atropine, which blocks the action of a neurotransmitter called acetylcholine. Acetylcholine regulates the nervous system’s activity, including muscle movement, heart rate, and glandular secretion. By blocking the action of acetylcholine, atropine disrupts the body’s normal functioning, leading to a range of symptoms such as dry mouth, dilated pupils, increased heart rate, and decreased sweating.
Another alkaloid in nightlock berries is scopolamine, which has powerful psychoactive effects and can cause hallucinations and delirium. Scopolamine is also a potent anticholinergic, which blocks the action of acetylcholine in the brain, leading to cognitive impairment and memory loss.
In addition to these alkaloids, nightlock berries contain solanine, a toxic chemical that can cause gastrointestinal distress, vomiting, and diarrhea. Solanine is also found in other poisonous plants, such as potatoes and tomatoes. It is particularly concentrated in the green parts of the plant.
The Toxicity of Nightlock Berries in Animals: What Pet Owners Should Know
Nightlock berries are one of the most poisonous plants in the world, containing a cocktail of deadly chemicals that can cause serious harm to the human body. The toxins in nightlock berries, known as alkaloids, affect the nervous system, leading to confusion, hallucinations, seizures, and even death.
The main alkaloid in nightlock berries is atropine, which blocks the action of a neurotransmitter called acetylcholine. Acetylcholine regulates the nervous system’s activity, including muscle movement, heart rate, and glandular secretion. By blocking the action of acetylcholine, atropine disrupts the body’s normal functioning, leading to a range of symptoms such as dry mouth, dilated pupils, increased heart rate, and decreased sweating.
Another alkaloid in night lock berries is scopolamine, which has powerful psychoactive effects and can cause hallucinations and delirium. Scopolamine is also a potent anticholinergic, which blocks the action of acetylcholine in the brain, leading to cognitive impairment and memory loss.
In addition to these alkaloids, nightlock berries contain solanine, a toxic chemical that can cause gastrointestinal distress, vomiting, and diarrhea. It is particularly concentrated in the green parts of the plant.
The Legal Status of Nightlock Berries: Restrictions and Regulations
Nightlock berries are a fictional fruit featured in the popular book series and subsequent movies, The Hunger Games. These poisonous berries play a significant role in the story’s plot, leading many readers to wonder about their legal status in real life. As these berries do not exist in the real world, there are no legal restrictions or regulations regarding their use or possession.
However, the concept of poisonous berries does exist in the real world, and there are regulations to prevent their harm to humans and animals. In many countries, selling or possessing poisonous plants or substances is illegal, and individuals found doing so can face legal consequences. Additionally, there are regulations for using poisonous plants in certain industries, such as medicine and agriculture, to ensure their safe and controlled use.
It is important to note that even in fictional works, portraying harmful or illegal actions can have a real-life impact. The popularity of The Hunger Games has led to an increase in interest in foraging and identifying wild berries, which can be dangerous if done improperly.
Conclusion
Nightlock berries are a fascinating and controversial plant with a long and storied history. While they have been used for centuries for their medicinal properties, they are also extremely toxic and can cause serious harm if ingested. Suppose you are interested in using nightlock berries for their potential benefits. In that case, it is important to do so under the guidance of a qualified healthcare provider who can help you use them safely and responsibly.
In summary, while nightlock berries do not have a legal status in real life, the concept of poisonous plants and substances is regulated to prevent harm. It is crucial to cautiously approach any plant or berry and follow applicable regulations and guidelines to ensure safety.
Apart from this, if you are interested to know more about Palo de Vibora then visit our Health category.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
· Are nightlock berries real?
No, nightlock berries are fictional plants that do not exist in the real world.
· Can nightlock berries be used for medicinal purposes?
No, nightlock berries are highly toxic and should never be consumed. There are no known medicinal uses for these berries.
· What are the symptoms of nightlock berry poisoning?
The symptoms of nightlock berry poisoning can include abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, confusion, hallucinations, seizures, and in severe cases, death.
· Can you die from consuming nightlock berries?
Yes, consuming nightlock berries can be fatal, especially if a large amount is ingested.
· How can you identify nightlock berries?
As nightlock berries are fictional, they cannot be identified in the real world.